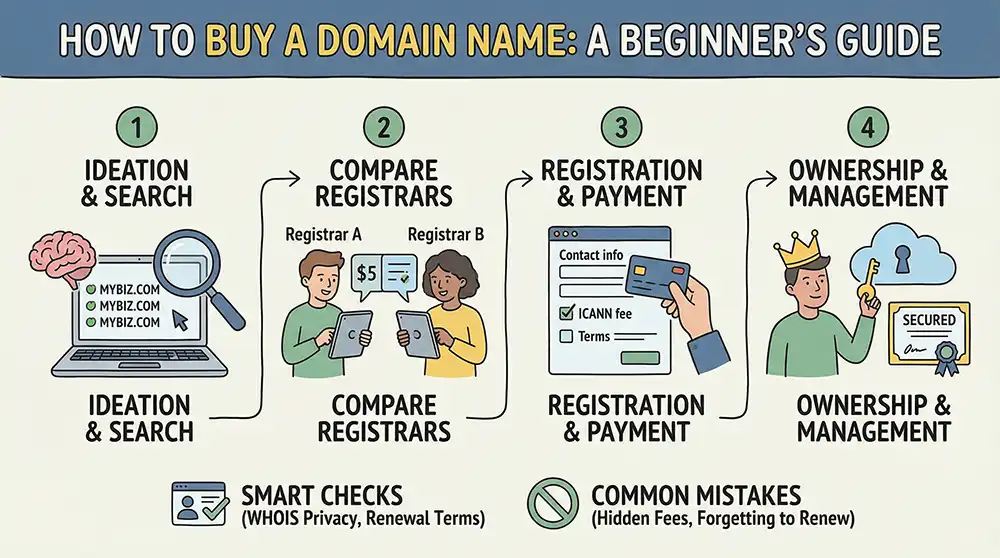
How to buy a domain name is one of the top questions new website owners ask when building an online presence. This guide is for beginners, small business owners, and creators who want to register their first web address with confidence. If you feel unsure about pricing, ownership rules, or which provider to choose, you are not alone.
Buying a web address can seem technical, especially with terms like ICANN, WHOIS, and registration periods. The good news is that the process is straightforward once you understand what you are actually purchasing and how renewals work. A few smart checks upfront can save you money and frustration later.
You will learn what it really means to register a domain, the exact steps to follow, how to compare registrars, and which common mistakes to avoid. By the end, you will know how to secure the right name and manage it properly.
Table of Contents
What it means to buy and register a domain name
Buying a domain name means registering a web address through an accredited domain registrar for a specific registration period. When you purchase a domain, you are not buying it forever but leasing the rights to use it for a set amount of time.
Once registration is complete, your contact details are recorded and the name is linked to your account. You can then connect it to a website, an email service, or other online tools. Control remains with you as long as you renew on time.
- You gain exclusive rights to use the name during your active registration period.
- You can transfer it to another provider if needed.
- You must renew it before expiration to keep control.
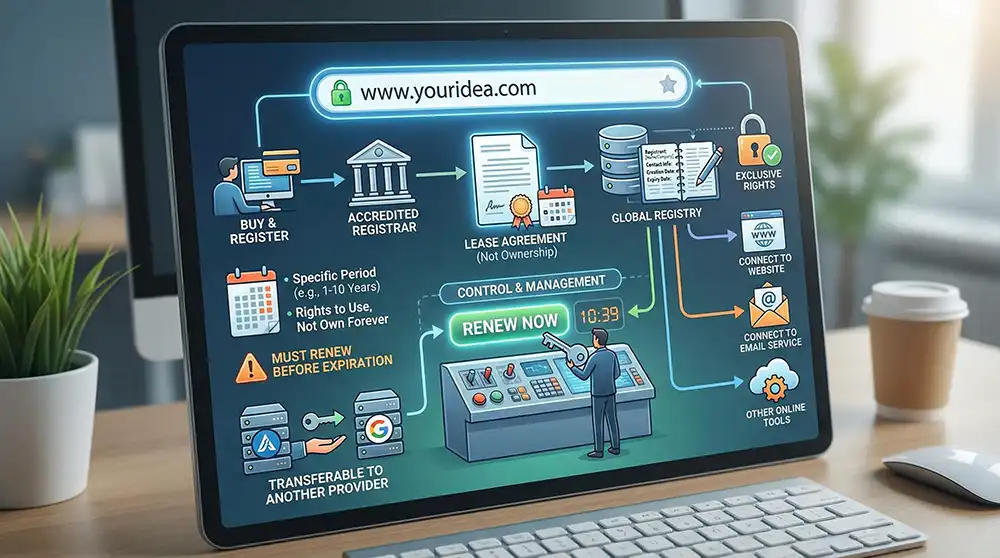
The role of an ICANN-accredited registrar
A domain registrar is a company authorized to sell and manage domain registrations. An ICANN-accredited registrar is approved by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers, the organization that oversees global domain rules and standards. Accreditation adds oversight and credibility to the registration process.
For example, Squarespace is an ICANN-accredited registrar and offers search and registration services. Wix is also ICANN-accredited for certain extensions such as .com and .net. Choosing an accredited provider helps ensure your registration follows recognized industry standards.
How to buy a domain name step by step
The process of how to buy a domain name includes searching availability, selecting a professional registrar, choosing a registration period, and completing payment. Once you understand what registration means, the practical steps are straightforward and build on each other.
- Search domain availability.
- Compare ICANN-accredited registrars.
- Check renewal pricing and registration period.
- Review included features such as privacy, SSL, and email forwarding.
- Enable auto-renewal after purchase.
Search availability and compare domain extensions
Start by using a registrar’s search tool to check whether your desired name is available. If it is taken, you may see alternative suggestions or different domain extensions. Domain extensions, also called TLDs, are the suffixes like .com, .net, or .org at the end of a web address.
Your choice of extension can influence branding and perception. Squarespace, for example, offers a wide selection of domain extensions, giving you flexibility if your first choice is unavailable. Consider how the full name looks, sounds, and feels before making a final decision.
Choose your registration period and complete payment
Every domain is registered for a defined registration period, typically ranging from one to several years. This time-based model affects both pricing and long-term planning. Some providers allow multi-year registrations, depending on the extension.
Wix states that domains can be registered for multiple years and notes that certain extensions such as .ai require a minimum two-year cycle. Promotional pricing may apply only to the first year, so review renewal terms carefully before checkout. Once payment is complete, the domain is added to your account.
How to choose a domain registrar and compare features
A domain registrar manages your registration, renewals, and technical settings. After reviewing the steps, the next decision is choosing the provider that fits your needs. Comparing features helps you avoid hidden costs and missing tools.
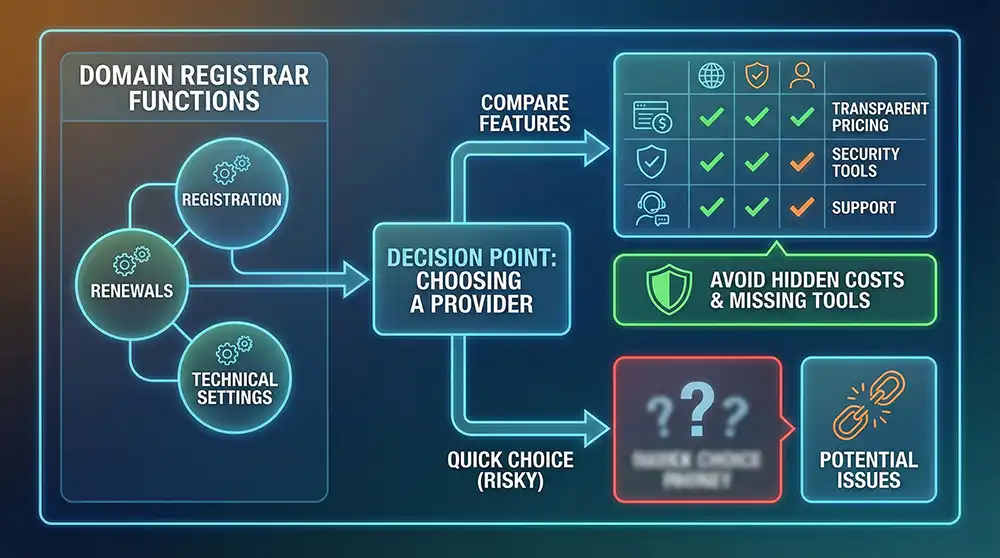
Included WHOIS privacy and SSL protection
WHOIS privacy hides your personal contact details from the public database associated with your domain. This can reduce spam and add a layer of protection for your personal information. Some providers include WHOIS privacy with eligible domains.
SSL certificates encrypt data between a visitor’s browser and your website, increasing security and trust. Squarespace indicates that WHOIS privacy and SSL certificates are included with eligible domains. Check what is included and whether any eligibility conditions apply.
Free domain offers and domain pricing models
Domain pricing varies depending on the extension, demand, and promotional offers. For example, Squarespace advertises limited-time offers such as select domains for $5 for the first year, including certain popular extensions. Renewal pricing may differ from the introductory rate.
Wix offers a free domain for one year with eligible annual website plans. After the initial period, standard renewal rates apply. Comparing first-year costs with long-term pricing gives you a clearer picture of the overall investment.
| Feature | Squarespace | Wix |
|---|---|---|
| ICANN-accredited status | ICANN-accredited registrar | ICANN-accredited for .com and .net |
| Free domain offers | Limited-time $5 first-year offer on select TLDs | Free for one year with annual plan |
| Included privacy and SSL | WHOIS privacy and SSL with eligible domains | SSL included with hosting |
| Registration period limits | Varies by extension | Multi-year options available; .ai requires 2+ years |
How to buy a domain name permanently?
Domain registration is time-based, which means control lasts only for the selected registration period and must be renewed. Many people wonder whether permanent ownership is possible, but it is not available.
You can register a name for multiple years in advance, depending on the registrar and extension. However, you must renew before expiration to keep it. If you do not renew, the name may become available for others to register.
- Registration grants usage rights, not permanent ownership.
- Renewals are required to maintain control.
- Auto-renewal reduces the risk of accidental expiration.
Common mistakes and myths when buying a domain
Common mistakes when buying a domain often involve misunderstandings about pricing, renewal rules, and included features. Even small details can make a difference, especially when promotional offers are involved.
Assuming the first-year price is the long-term cost
Promotional offers often apply only to the first year. Limited-time deals may advertise a low introductory rate for select extensions, but renewal pricing after the first year can be higher. Review the terms carefully before completing your purchase.
Believing you own the domain forever after payment
Paying for a domain does not grant lifetime ownership. Instead, you secure rights for a specific registration period. Some providers allow multi-year registrations, but renewal is still required at the end of that term.
- The first-year promotional price is the long-term cost.
- You own a domain forever after one payment.
- All registrars include the same features.
Frequently asked questions about buying a domain
Can you buy a domain name permanently
No, domain registration is time-based. You can register for multiple years, but you must renew to maintain control.
How much does it cost to buy a domain name
Domain pricing depends on the extension and any active promotions. Some providers advertise limited-time first-year offers, while renewal rates may differ.
Are there free domain name options
Yes, some website builders include a free domain for the first year with eligible annual plans. After that period, standard renewal fees apply.
What features are included with domain registration
Included features may consist of WHOIS privacy, SSL certificates, and email forwarding. Availability can depend on the registrar and the specific extension.
How long can you register a domain for
Registration periods vary by extension and provider. In many cases, multi-year registration options are available, though some extensions require minimum multi-year terms.
Key Takeaways
Registering a domain involves choosing an available name, selecting an ICANN-accredited registrar, deciding on a suitable registration period, and reviewing pricing and included features. The process is simple once you understand that registration is time-based rather than permanent.
Compare first-year promotions with renewal pricing, confirm what features such as WHOIS privacy and SSL are included, and enable auto-renewal to protect your investment. With these steps, you can secure your web address confidently and avoid common mistakes.
Relevant Internal Links
- What is a DNS?
- Most Popular Domain Registrars
- How to Find DNS Provider
- DNS Record Types You Must Know